+Welcome back Mrs. González! How was the travel?
-It was really long
+Oh, You must be very tired, I think must not very happy
-I'm actually very happy, I really like long travels.
+Oh, it's okay, You have any
backage?
-Yes, I have a Lot of backage
+It's not a problem, I can help you.
-That's really Nice! Thank You!
+ Now you must be in your Home.
- it's a good idea, in fact i'm getting tired
+ let's go!!!!
Was - Were
The verb "to be" is used in the simple past with a noun, an adjective or a prepositional phrase:
Was and were are the simple past tense of the verb to be
was is used for I, he, she, it and were is used for you (singular and plural), we, they.
Example:
I was away for the weekend
She was my school psychologist
They were play soccer with their cousins
We were champions in the basketball tournament.
Affirmative
Andrea was very tired
Andrea and Carlos were best friends
He was sick yesterday
They were hungry
Negative
Andrea wasn’t very tired
Andrea and Carlos weren’t best friends
Interrogative
For example:
Was Andrea very tired?
Yes, she was
No, she wasn’t
Were Andrea and Carlos best friends?
Yes, they were
No, they weren’t
Wh-question
For example
Where were you last week?
I was at University
How were your day?
My day were good
PAST SIMPLE
Refers to actions that occurred, which were completed in the past.
There are regular and irregular verbs.
REGULAR VERBS
In the case of regular verbs, the ending ed is added to form the past tense. It is very important the pronunciation. For example.
With infinitives ending in p, f, k or s (voiceless consonants, except t) we pronounce the ed ending as a "t".
With infinitives ending in b, g, l, m, n, v, z (voiced consonants, except d) or a vowel, we pronounce only the d.
Ruler
1. verb ends in "e", d is added to form the past tense, example:
- I decided to buy the red one
- She loved you
2. verb ending in y preceded by a consonant, change the y to "i" and add the ed. For example: try -tried, worry - worried, apply - applied.
- I was worried about your dog
- He applied the mathematical formula to the problem
3. If the verb ends in a short vowel and a consonant except y or w), we double the final consonant. Examples:stop - stopped , commit - committed
- He committed to his job
- He stopped at a red traffic light
IRREGULAR VERBS
Irregular verbs do not follow defined rules for forming the simple past tense
- They went for a walk in the park
- He brought a surprise gift for my birthday.
- Carlos said he could not go home
Affirmative sentences
For example:
- I brought my dog home
- My dad made arrangements to build the house.
- Carolina lent me her calculator
- He asked me about you
- We enjoyed the ride
Negative sentences
Fo example:
- I didn't read that book
- My dad didn't build my house
- Carolina did not lend me the calculator
- I did not spend all my savings
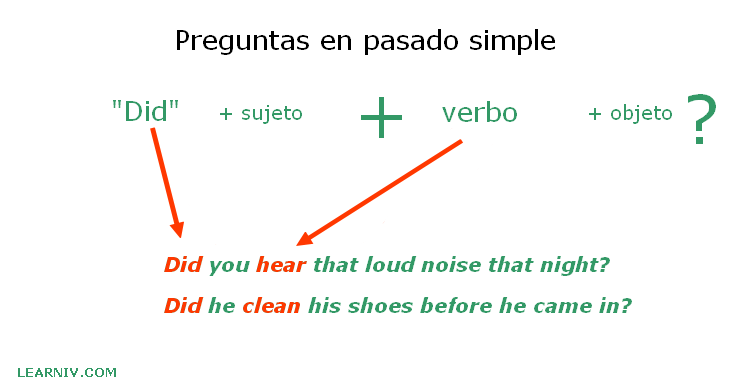
Interrogative sentences
For example:
- Did I spend all my savings?
No, I did not
- Did my dad build my house?
No, he did not
- Did you draw that portrait?
No, I did not
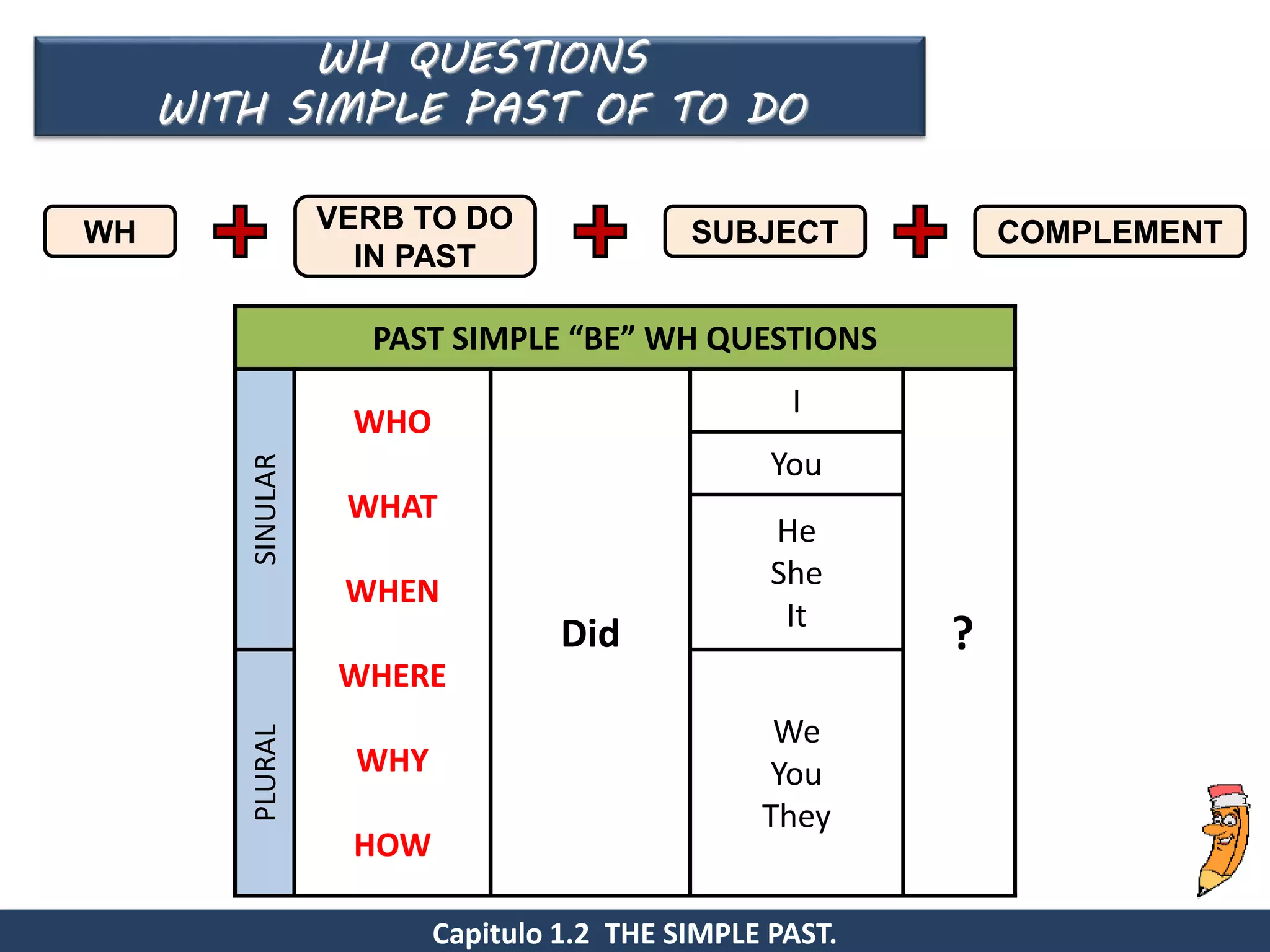
Wh questions:
For example:
- When did I draw that portrait?
- Where did they publish the new ?
- what did you send me in the mail?
All the information you asked me for yesterday
On my vacations I traveled to Tolu with my whole family, we went to the beach, we ate delicious, we bought seafood, we rode on the worm and the donut, I collected snails, . we also knew many places, we played volleyball, we got up early to go running on the beach and my uncle took bikes then we went out to see the sunrise and even camped, with bonfire, super nice. It was my favorite trip, I wish it could be repeated.
Clothes
What are the people in the photo wearing?
In the first image, the girl is wearing a red hat, a gray crewneck, a red skirt that matches her hat, a yellow handbag and brown loafers.
In the second image, the boy is wearing a yellow T-shirt with red stripes, blue pants and has red shoes. On the other hand, the girl is wearing a pretty pink dress with pink boots and has two purple bows in her hair.
They wear outwear, gloves, scarf, coat, sweaters and wear hosiery, as socks or maybe tights and jeans. They wear woolen cap for cold
They are wearing black and colorful shorts and tehuelche are T-shirts, sunglasses, one of them has a chain, shoes, running shoes, windbreaker
He wears a formal clothes, white T- Shirt black jacket, socks, oxfords. he has a watch and grey pants
VOCABULARY
Outwear bathubes
wear running pants
sweaters v- neck
underwear pums
boxers suit
bras blouse
panties trousers
tights trainers
pantihose bracelet
hosiery sunglasses
purses glasses
pajamas necklace
nightgowns earrings
watch piercing
earcuff tiara
ring scrunchy
COMPARATIVE
Used to compare differences between two objects persons or animals it is used to compare characteristics or qualities
Structure
Noun (subject) + verb + adjective in comparative degree + than + noun (object)
I am taller than my brother
Brazil is bigger than Spain
The word than is a conjunction that means 'that' in Spanish and serves to join the two parts of the comparison.
RULER:
If the adjective ends in consonant + vowel + consonant, the last consonant must be repeated before adding the ending.
For example:
Andrea is sadder today than yesterday
My dog is cuter than yours
This book is more interesting than the previous one
My bag is heavier than ever
Irregular comparatives:
This is blouse more expensive than pants
This sweater is less than that one.
Running is better for your health
OBJECT PRONOUNS
Object personal pronouns replace a noun to avoid repetition. The main difference with personal pronouns is that while the former replace a subject, the latter do not.
The main characteristic is that they follow a verb or a preposition (in, for, with)
For example:
Melissa asks to her, and she says: Her has a better book that can help us with homework.
You want to buy it or is just curiosity?
Music is everything for her.
Samuel is doing his homework . Leave him alone.
She and her brother are nice, I am studing with them